Streamlining Bioprocess

Image reference: / source
WHAT IS BIOPROCESS?
Bioprocess is the process of translating biological science into bio-based products, processes, or systems. It plays a major role in the production of biotherapeutics, vaccines, speciality chemicals, biochemicals and enzymes. This involves a series of upstream and downstream processes, which are interdependent and connected to each other, mostly in a linear manner.
The market for bioprocess derived products is steadily increasing. However, only 21 biologics were approved by the FDA in 2018, 22 in 2019, and 8 in 2020[1].
Incorporating Quality-by-Design (QbD) into the process and building it into the product is being actively pursued to innovate, improve development strategies, and enhance the success rate of drugs towards the final stages of development. Automation in bioprocessing has been one of the significant contributors to ensuring QbD in different stages of drug development.
WHATS THE FUTURE?
In bioprocess, the channelling of data from one step to another plays an integral and crucial part in the process.
Informatics platforms like ELN, LIMS etc., can play a significant role in pipelining data transfer in these processes. They enable automation of the workflow, collaboration with multiple systems and users, parallelizing data capture and analysis, and documentation of data[2]. In other words, digitalization of the processes ensures streamlining of data across different experiments while also maintaining source data credibility and traceability.
Other platforms such as SDMS, LIS, Instrument Integrations, Registration systems etc., can integrate to establish a digital footprint of the entire lab.
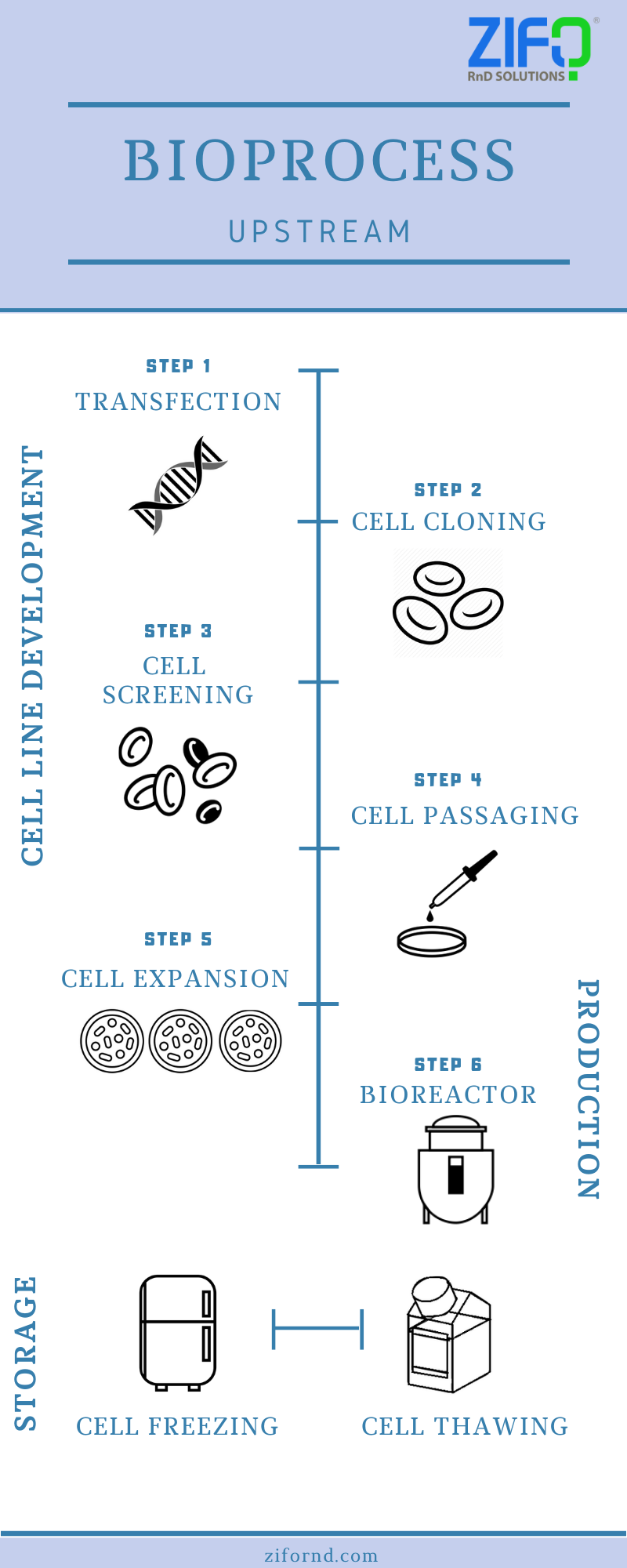
Bioprocess can be broadly classified into two stages – upstream and downstream processing.
The upstream processing is the phase in which cell lines are generated and biomass is produced at an appreciable scale.
The downstream processing, on the other hand, is the phase that deals with the extraction or separation of desired products from the biomass (developed in upstream processing). The image shows the processes involved in the upstream phase.
Digitalization of the upstream processes ensures transparency and traceability. It can function as an integrated bioprocess execution system, with the following advantages[2]:
Scientific and laboratory informatics platforms aid in the following:
- Enable system integrations and facilitate data transfer among systems.
- Provide a secure repository for data handling.
- Flexible to create or amend lab processes and procedures.
- Enforce lab protocols, regulatory processes, and business standards.
These digital platforms hence prevent common laboratory and documentation errors, thus building QbD from the very initial stages of bioprocesses. Informatics platforms provide continuous feedback that supports the entire process lifecycle, facilitating its evolution and optimization.
Process efficiency, achievable cell densities and product titres in cell culture processes can be increased enormously through the application of innovative technologies.
Automated cell culture systems, single-use bioreactors, integrated online biomass measurement and other latest applications help bioprocess move towards better performance.
WHATS NEXT?
Significant progress can be achieved by integrating workflows. With newer advances in processes and technology, adaptation to informatics platforms proves to be the most suitable option. These platforms and solutions are constantly updated and upgraded to support and meet the emerging trends in bioprocess studies.
Stay tuned to know more about the influence of digitalization on downstream processing…
References:





